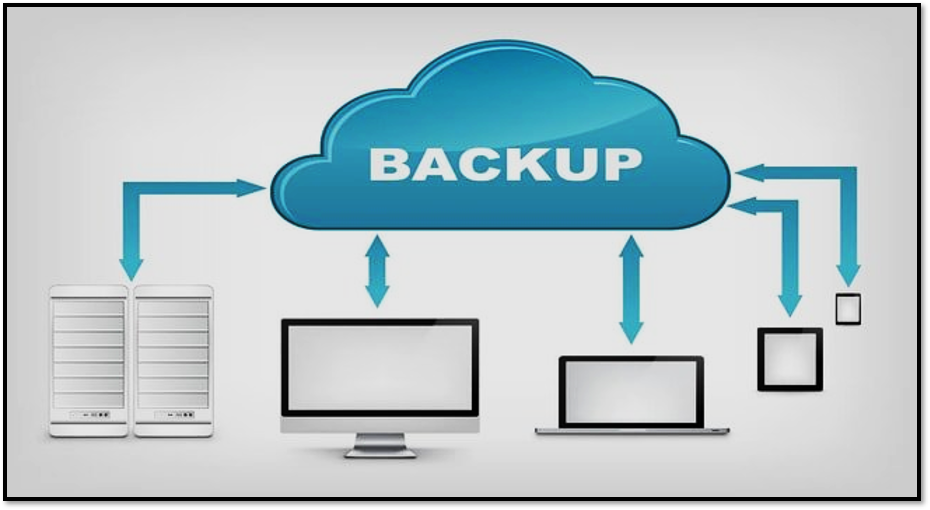
Traditional Backups are not enough. Why?
1. All of us Knows that data is a critical asset and its growth is exponential. You can think about an unfortunate situation where your system crashes & you no longer have access to your business-critical data. The cause for this is any from malware attacks, accidental file deletion or even natural disasters. But it has the same consequence, i.e., halted business operations leading to reputation & revenue loss.
2. The events of the previously mentioned situations, basic information should be accessible to accomplish business congruity. You can secure your information by different methods yet Backup and Disaster Recovery assumes a vital part in information assurance – a fundamental factor. Subsequently, organizations are consistently keeping watch for present day reinforcement answers for their modernized IT.
3. Beforehand, backing up basic information included utilizing Tapes. One of the vital benefits of tapes is cost. You can store a lot of information with less use.
4. The most common storage media to store backups after tapes, are Disks.
5. Disks are altogether productive than tapes in view of its quicker access speed, less moving parts, and the consideration of extra highlights like deduplication to utilize capacity effectively.
6. The pattern of putting away reinforcements on Disks has been changing since an ever-increasing number of individuals are picking On-Premises Data Storage.
7. On-Premises Data Storage offers progressed security for your information, gives you the adaptability to get to your information from anyplace whenever. After some time, the general reinforcement strategy is changed from Tape to Disks to On-Premises Data Storage. Despite the fact that they have various benefits, every one of these capacity media has its own downsides.
8. The consecutive read/compose fundamentally lessens the speed in tapes. Further, there are likewise risks for tapes to corrupt over the long haul which can make data difficult to reach. With regards to Disks, they have not many requirements like short life expectancies, and furthermore a possibility for high disappointment rates. These reasons make tapes and circles temperamental. While On-Premises Data Storage is solid with cutting edge safety efforts carried out.
Your IT foundation is getting modernized, contingent exclusively upon any of these capacity media for your reinforcements is more similar to leaving an opportunity for your business information to be in danger. All that you will require is an answer that will assist you with using the advantages of every storage media while keeping your business consistently accessible.
Benefits of SAN and LAN Storage :
Let’s have a look at few Benefits of SAN and NAS Storage.
The SAN and NAS Storage such as Synology, Fujitsu, HPE, Net Gear, NetApp, Dell EMC, IBM and Hitachi Data Systems are provided by companies.
Disk Utilization
1. Many people consider this to be being the primary advantage of SAN and NAS storage. In case you're utilizing traditional direct storage, you'll possibly get usage of around 30%. At the point when we utilize centralize storage, we can draw a figure which is nearer to 80%. Suppose that we have 50 servers which we expect will each require 300GB of extra storage. Well in case you're utilizing DAS, you're not going to place in precisely 300GB of Disks capacity limit in every one of those servers, you're likely going to place in 500GB in light of the fact that you need to leave a touch of space for surprising development. Fitting bigger disks in a server will require an outage and is truly badly arranged.
2. With centralize storage capacity, we don't have that issue. We have one centralize pool of capacity, and we can cut it up and disseminate it to the various servers precisely how we need to and effectively transform it on the fly. So on the off chance that We got a few servers that require 300GB circle space, we can give them 300GB plate space. Assuming later on incidentally, they need more space, We can undoubtedly give them it when they need it. Ordinarily, we can do this non-problematically. Furthermore, we move from 'For good measure' to 'Without a moment to spare' - setting aside cash since we don't have to purchase the actual plates until they're really required.
Thin Provisioning
1. This is straightforwardly identified with Disk Utilization. Suppose that We have 10 servers, and we believe that they may require up to 500GB of extra storage space. 10 server's x 500GB storage = 5TB of capacity required. In a traditional environment, we would have to purchase the full 5TB of Disk space that may be required later on this moment. However, when I'm utilizing unified capacity, we can execute slim provisioning.
2. Suppose that the servers are simply going to at first be utilizing 200GB of extra room each. 10 server's x 200GB storage= 2TB limit. With meager provisioning, we purchase just the 2TB of capacity that will be utilized now, however we make it look to the servers as though they really have the full 500GB each. It would seem that there's 5TB extra room there, yet We've just really paid for 2TB, and when they do require the extra space, we purchase the plates around then. I'm moving from a 'for good measure' model of buying extra room, to a 'without a moment to spare' model. This gives cost reserve funds on equipment, rack space, force and cooling, and the reserve funds are duplicated as hard circle cost will in general descend over the long run.
Deduplication and Compression
This gives extra storage effectiveness. We have numerous servers all utilizing a similar centralize storage, if there's any blocks on disks that are rehashed, we can eliminate those copy blocks and simply keep one duplicate. Also, we can utilize pressure at the document level to diminish the measure of room utilized and get a similar advantage. For workloads which have high measures of duplication and compressible information, (for example, virtualized conditions where numerous virtual machines have a similar working framework, patches and applications) this can give enormous investment funds in the measure of circle space required.
Resiliency
Centralized storage systems are built to have high degrees of resiliency as they will almost & almost be mission critical systems for the companies. If a disk fails then it taken care of by RAID, if a disk shelf fails that's taken care of by mirroring. If a controller fail, we have a redundant peer controller which can take over, & we can replicate data between storage systems in various sites which give us backup in case we lose the entire data center.
Centralized Management
If you have got 50 servers, which is much simpler to manage the storage for all of them if that's on one centralized system, rather than distributed individually to each of those 50 servers.
Centralized Backup
Managing backups is very inconvenient and time-consuming process, if we have 50 different tape drives on our 50 different servers & we're managing them all individually. If we're consolidated on centralized storage, then we can centralize backup solution as well which is much simpler to manage. Storage systems can also backup to remote disk which reduces space requirements and backup windows and doesn't require loading/unloading of physical media.
Snapshots
Snapshots are a point in time copy of the file system. These can be used as a convenient short-term backup. Snapshots consist of pointers to the original blocks on disk rather than being a new copy of the data, so they initially take up no space and occur nearly instantaneously. If data gets corrupted or if somebody accidentally deletes a file, then we can very quickly recover using snapshots
Disaster Recovery
We can replicate data from main site to a disaster recovery site giving us a backup if the main site fails. We can also load balance incoming client requests for read-only data between the different sites.
Virtualization Support
Software such as VMware and Hyper-V allow businesses to run multiple virtual servers on the same underlying physical hardware server. We can have a Linux web server, Exchange mail server and SQL database server all running on the same physical box. For example, and this is transparent to each of those virtual servers. The main feature of virtualization software is the ability to move virtual servers between physical servers on the fly while they are still running. This mean that the virtual servers can keep on running with no outages even if it's underlying physical server fails or is taken down for maintenance. External storage is a requirement for this feature.
Diskless servers
A SAN protocol can have servers boot up from disks on the remote storage. They don't have to have a single disk drive in the servers themselves. This is a very famous option with blade servers. Hence this gives savings in hardware costs, rack space, power and cooling.
Storage Tiering
The disks in the system with differing performance, such as high-performance SSD drives, and high-capacity SATA drives. We can keep hot data which is accessed frequently on the SSDs, and older archived data on the SATA drives. Many of the storage systems have features which can automatically move the data from high performance to lower performance disks as it's being accessed less frequently over time.